The ETZ Conference 2025
The ETZ Conference 2025
by İdil Ertuğan and Esra Gün Alayafi
The ETZ Conference, held on March 1st, 2025 in İstanbul brought together professionals, experts, and enthusiasts from various industries to discuss the latest trends, advancements, and challenges in their fields. The event provided opportunities for networking, knowledge sharing, and collaboration. While it fulfilled its purpose in many respects, some areas could benefit from adjustments to improve the overall experience for participants in the future.
Prof. Dr. Sahin Albayrak’s Presentation: AI - Past, Present & Future
Prof. Dr. Sahin Albayrak, a leading AI expert, provided insights into AI's evolution, current applications, and future prospects.
The Past: Foundations of AI
AI began in the 1950s with symbolic AI and rule-based logic. However, progress slowed during two “AI winters” due to limited advancements. The 1990s saw a shift toward machine learning, enabling AI to learn from data, and laying the foundation for modern AI.
The Present: AI in Action
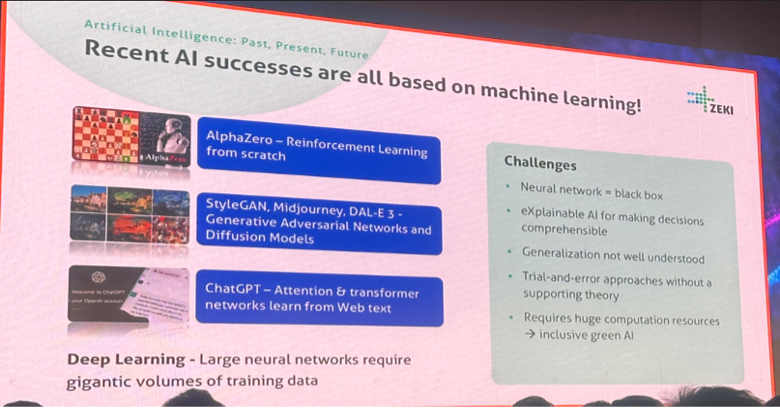
Today, AI powers technologies like natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, robotics, and healthcare applications. AI-driven solutions are transforming industries, while ethical issues such as bias and privacy remain concerns. Prof. Albayrak’s team has also successfully tested a driverless bus, showcasing AI's growing role in automation.
The Future: AI’s Potential and Challenges
AI’s future includes the possibility of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), though significant hurdles remain. Human-AI collaboration will enhance decision-making in fields like healthcare and finance. AI is also expected to play a major role in personalized education. Prof. Albayrak emphasized the importance of ethical AI development to ensure fairness and accountability.
UNESCO's AI Competence Frameworks for Students and Teachers
by DR. FENGCHUN MIAO
The increasing influence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in various sectors is reshaping education, requiring both students and teachers to develop a strong understanding of AI competencies. In response, UNESCO has developed AI competence frameworks (AI CF) to help guide the development of AI education globally. These frameworks define the knowledge, skills, and attitudes required to effectively interact with AI technologies in educational contexts, emphasizing ethical and human-centered AI development. The framework is supported by detailed matrices that outline competencies by grade level and teacher role, as well as guidance from leading AI initiatives such as China's AI curriculum development.
UNESCO’s AI Competence Framework for Students (AI CFS)
The AI Competence Framework for Students (AI CFS) defines the essential AI competencies that learners need to develop. It recognizes that students of all ages should not only learn about AI but also understand how AI systems work and their implications in society. The framework addresses AI literacy as a crucial skill for the future, focusing on the responsible and ethical use of AI.
The AI CFS has two main dimensions:
AI Literacy and Skills: This dimension covers technical AI knowledge, such as understanding algorithms, machine learning, and data analysis. It ensures students know how AI systems operate and how to apply AI tools in solving real-world problems.
Ethical and Societal Impact: This dimension focuses on the ethical implications of AI technologies. It emphasizes the importance of privacy, bias, fairness, and transparency in AI applications. Students are encouraged to think critically about how AI impacts their lives, their communities, and society as a whole.
These two dimensions are broken down into various competencies across different grade levels, with particular emphasis on ethical awareness, problem-solving, and interdisciplinary applications.
AI CFS Two-Dimension Matrix
The AI CFS matrix provides a structured approach to understanding the competencies required by students, broken down into technical competencies and ethical competencies:
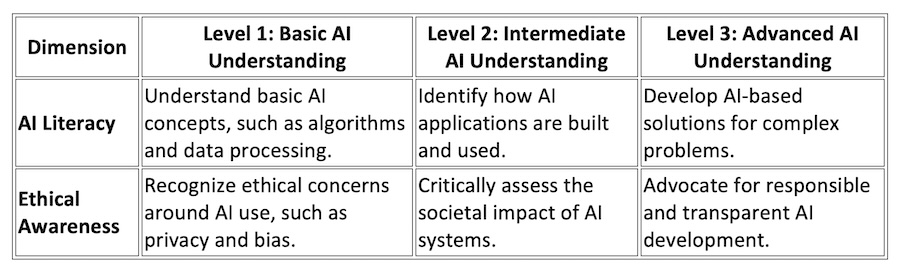
This matrix helps to create a clear learning progression for students, enabling them to become not only competent users of AI but also informed and ethical participants in the AI ecosystem.
UNESCO’s AI Competence Framework for Teachers (AI CFT)

The AI Competence Framework for Teachers (AI CFT) equips educators with the competencies needed to teach AI to students and integrate AI tools into their teaching practice. AI CFT is structured around a matrix that highlights key areas of competency development for teachers, including:
Understanding AI: Teachers need foundational knowledge of AI technologies and how they are being used in educational tools.
Integrating AI in Education: Teachers must learn how to use AI-powered tools to enhance teaching and learning. This includes using AI for personalized learning, assessments, and adaptive learning environments.
Teaching AI to Students: Teachers need strategies for teaching AI concepts and skills, adapting the curriculum to different age groups and learning levels.
Ethical Implications of AI: Teachers are encouraged to explore the societal and ethical implications of AI with their students, preparing them to critically engage with AI applications in their future careers and daily lives.
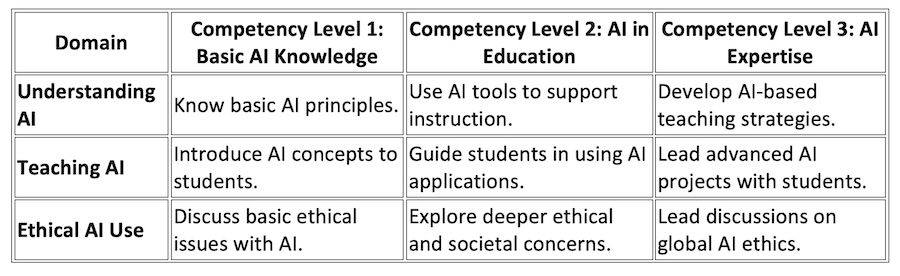
AI CFT Framework Matrix
The matrix divides AI competencies for teachers into three key domains:
This matrix ensures teachers have a clear path for professional development in AI, ensuring they can confidently integrate AI into their classrooms.
Here's the information in a table format:
In line with UNESCO’s global vision, China’s National ICT Curriculum Standard for Upper Secondary Schools (2024) outlines the development of AI literacy and competencies at the upper secondary level. The curriculum aims to prepare students for future careers by developing advanced skills in computational thinking, machine learning, robotics, and data analysis. It emphasizes problem-solving and the application of AI technologies in real-world scenarios.
China's ICT curriculum is structured around the following key AI-related areas:
AI Fundamentals: Understanding the basics of AI, including algorithms, data processing, and machine learning concepts.
Practical AI Applications: Hands-on experience with AI tools and platforms for tasks such as coding, automation, and robotics.
Ethical AI Use: Analyzing the ethical implications of AI technologies, with a focus on privacy, security, and societal impact.
China’s AI Curricula Grade by Grade
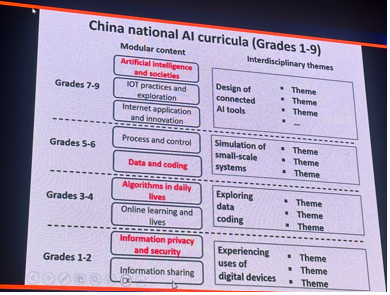
China’s AI curriculum development has been structured to progressively build AI knowledge from lower to upper secondary levels. The following is a grade-by-grade breakdown:
Grade 7-8 (Lower Secondary): Introduction to AI concepts, such as basic algorithms, problem-solving with computers, and understanding the use of AI in daily life.
Grade 9-10 (Intermediate Secondary): More advanced topics, including basic programming with AI tools, understanding machine learning concepts, and exploring the use of AI in industries like healthcare and manufacturing.
Grade 11-12 (Upper Secondary): Focus on specialized AI topics, including neural networks, robotics, data science, and practical projects where students create AI models or applications.
UNESCO's AI competence frameworks for students and teachers emphasize a comprehensive approach to AI literacy, combining technical skills with ethical understanding. China’s national curriculum aligns with this by providing a structured progression in AI education, ensuring students develop the necessary skills at various levels. Both frameworks aim to prepare students and teachers to navigate the future responsibly, balancing AI's technical aspects with its ethical implications.
